ROS 2
This tutorial assumes you have either pre-installed ROS 2
or launched the included VS Code development container. For more details, please see .devcontainer/readme.md.
Note
Before proceeding, please install the Reach Robotics SDK. Instructions for installation can found in the Getting Started section.
Setup
First, source the ROS 2 underlay:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Note
It can be convenient to automatically source this script every time a new shell is launched.
echo "source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
Keep in mind, if you have more than one ROS distribution installed, ~/.bashrc must only source the setup.bash for the version you are currently using.
Build the ROS 2 packages:
cd ~/workspace
colcon build
Source the ROS 2 overlay packages:
source ~/workspace/install/local_setup.bash
At this point the Reach Robotics nodes have been built and are ready to use.
Note
If you are using a ROS 2 distribution other than Foxy, you’ll need to modify the source
command accordingly. I.e. `source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash`
Packages
The ROS 2 folder is split into several packages. Each package is briefly described below.
rs_passthrough
The RS passthrough is the core package that facilitates communication to Reach
Robotics products. This passthrough converts ROS 2 messages into Serial or UDP
packets that can be read by the connected product. Each node in the passthrough
uses rs_msgs/Packet for messaging. The packet construct is defined as:
uint8 device_id
uint16 packet_id
uint8[] int_data
float32[] float_data
where device_id is the device identifier, packet_id is the packet identifier,
int_data is a list of 8 bit integers representing the integer data to be sent, and
float_data is a list of 32 bit floating point numbers representing the floating point data
to be sent. It’s important to note, that only one of int_data or float_data should be
populated in a given packet.
To launch the passthrough, run:
ros2 run rs_passthrough serial_passthrough --ros-args -p serial_port:=</dev/ttyUSB0>
where,
serial_port(string) - Serial Port to connect to the arm (Defaults to “/dev/ttyUSB0”)baudrate(int) - Baudrate port of the serial connection. (Defaults to 115200)
ros2 run rs_passthrough udp_passthrough --ros-args -p ip_address:=192.168.2.4 -p port:=6789
where,
ip_address(string) - IP Address of the arm. (Defaults to 192.168.2.3)port(int) - UDP Port of the arm. (Defaults to 6789)
For both passthrough nodes, the published topic and the subscribed topic, respectively, are:
/rx(rs_msgs/Packet) - Received Packets from the manipulator/tx(rs_msgs/Packet) - Packets that will be sent to the manipulator
Examples
This example demonstrates how to request read actuator telemetry from a manipulator.
To launch this example, run the launch file.
ros2 launch rs_passthrough serial_passthrough_example.launch.py serial_port:="/dev/ttyUSB0"
ros2 launch rs_passthrough udp_passthrough_example.launch.py ip_address:=192.168.2.4 port:=6789
The script communicates to the passthrough node via the /tx and /rx topics.
It publishes request packets to the /tx topic at a set frequency.
It subscribes the to /rx topic and listens for position packets.
reach_bravo_description
Reach Bravo Description package contains the Universal Robot description File (URDF) files for the Bravo range of manipulators.
Supported Products:
RB-7002 - Reach Bravo 7 (PRO)
RB-5002 - Reach Bravo 5 (PRO)
Examples
Examples of viewing URDFs in RVIZ.
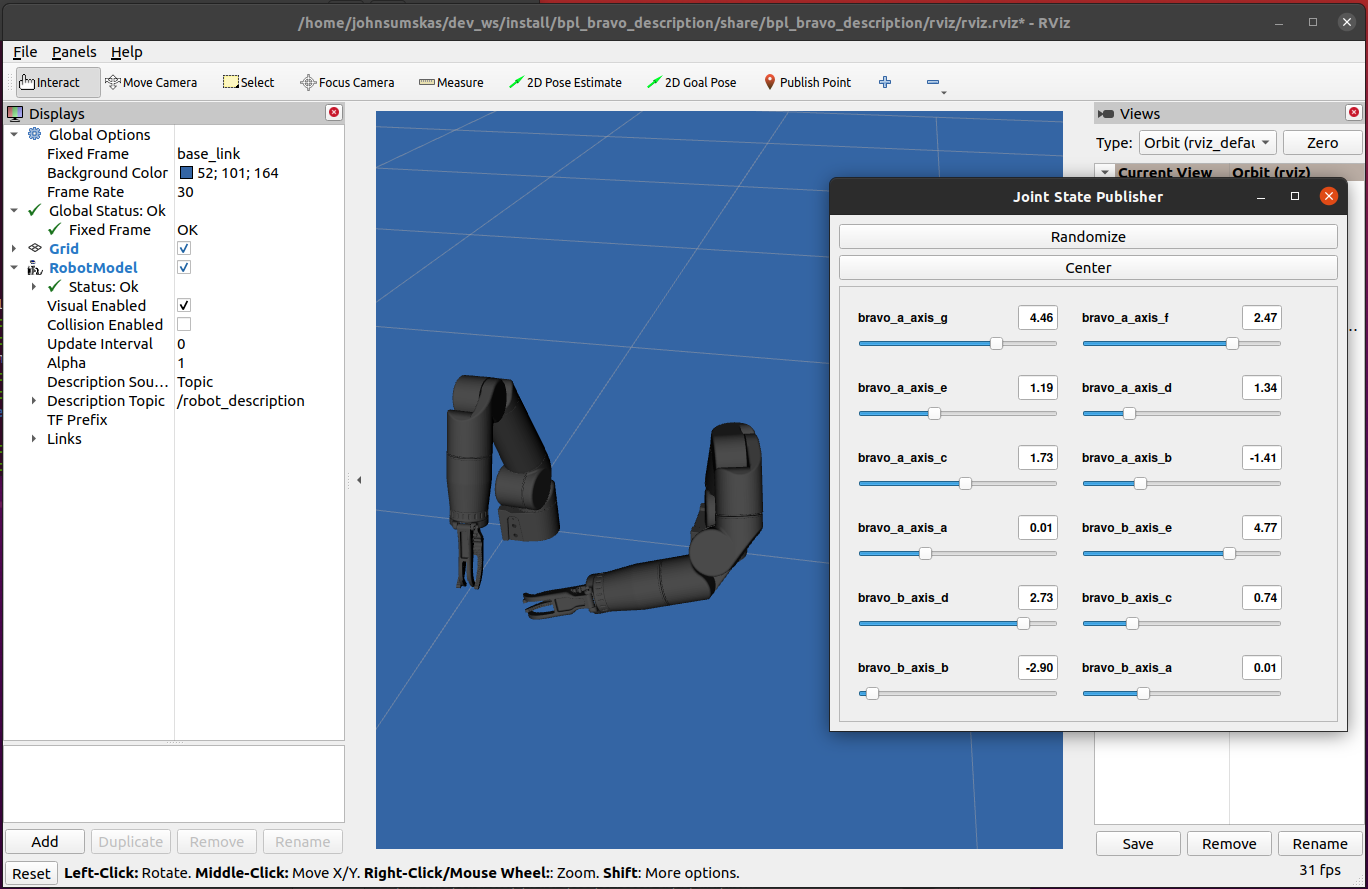
Viewing a Bravo 7 URDF:
ros2 launch reach_bravo_description view_bravo_7.launch.py
Viewing a Bravo 5 URDF:
ros2 launch reach_bravo_description view_bravo_5.launch.py
Viewing a Bravo 5 and Bravo 7 URDF:
ros2 launch reach_bravo_description view_bravo_double.launch.py